|
|
(64 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown)
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | '''Warning: RPi support should be considered as experimental. Be prepared to face issues if you try GIMX on the RPi.''' | + | <languages /> |
| | + | <translate> |
| | + | <!--T:1--> |
| | + | '''Warning: RPi support should be considered as experimental. The USB controller has been unstable since the first version. Be prepared to face issues if you try GIMX on the RPi.''' |
| | | | |
| | GIMX can run on many Linux targets, and the [http://www.raspberrypi.org/ the Raspberry Pi] is one of them! | | GIMX can run on many Linux targets, and the [http://www.raspberrypi.org/ the Raspberry Pi] is one of them! |
| − | == Tested setup ==
| |
| − | * Raspberry Pi: model B, 256MB
| |
| − | * Distro: [http://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads Raspbian wheezy] (2013-07-26-wheezy-raspbian)
| |
| − | * '''Self-powered USB hub''': Belkin 7 ports F4U017 (self-powered = with an external power supply)
| |
| − | * Keyboard: n25te plugged on the USB hub
| |
| − | * Mouse: Logitech G500 plugged on the USB hub
| |
| − | * PS3: FAT - FW 4.41
| |
| | | | |
| − | * Bluetooth dongle: Pluscom BT20 (CSR Bluecore4-rom) plugged on the USB hub
| + | == Setup using pre-made image == <!--T:23--> |
| | | | |
| − | * DIY USB adapter: Teensy 2.0 + CP2102 plugged on the USB hub
| + | <!--T:24--> |
| | + | The simplest way to set up GIMX on a Raspberry Pi is by flashing a pre-made image. See forum user steel_3d's instructions on getting up and running: [http://www.steve-marton.com/gimx/?p=462 Build your own Plug n Play GIMX emulator using Raspberry Pi] |
| | | | |
| − | == Fix for USB issues == | + | == Hardware considerations == <!--T:23--> |
| − | A firmware update is required to fix USB issues (missing mouse & keyboard events - [http://www.raspberrypi.org/phpBB3/viewtopic.php?t=39175&p=347278 source]).
| |
| | | | |
| − | Type the following command '''and reboot''':
| + | <!--T:24--> |
| − | sudo rpi-update
| + | Use a USB HUB only if there are no ports available on the RPi.<br /> |
| − | Once the rpi is rebooted, check that the RPi is running the right kernel by typing:
| + | It is highly recommended to use a HUB with an external power supply. |
| − | pi@raspberrypi:~$ dmesg | grep dwc_otg
| |
| − | The following line should be present in the output:
| |
| − | dwc_otg: FIQ split fix enabled
| |
| − | Tested Rpi firmware:
| |
| − | pi@raspberrypi ~ $ uname -a
| |
| − | Linux raspberrypi 3.6.11+ #541 PREEMPT Sat Sep 7 19:46:21 BST 2013 armv6l GNU/Linux
| |
| − | pi@raspberrypi ~ $ /opt/vc/bin/vcgencmd version
| |
| − | Sep 10 2013 12:45:45
| |
| − | Copyright (c) 2012 Broadcom
| |
| − | version 26ff70fafc90598f8cf7666117c00acb25b03110 (clean) (release)
| |
| | | | |
| − | == UHID kernel module == | + | == USB adapter using the on-board UART interface == <!--T:6--> |
| | | | |
| − | If you plan to use a Logitech force feedback wheel, you will have to build the uhid.ko module for your kernel.<br />
| + | === Hardware requirements === <!--T:25--> |
| − | Install the right version of gcc, as explained here: [https://github.com/notro/rpi-source/wiki link].<br />
| |
| − | Update your kernel:
| |
| − | <pre>sudo rpi-update</pre>
| |
| − | In case the kernel was updated, reboot:
| |
| − | <pre>sudo reboot</pre>
| |
| − | Install the rpi-source tool:
| |
| − | <pre>sudo wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/notro/rpi-source/master/rpi-source -O /usr/bin/rpi-source && sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/rpi-source && /usr/bin/rpi-source -q --tag-update</pre>
| |
| − | Run rpi-source:
| |
| − | <pre>rpi-source</pre> | |
| − | This step may take a while to complete.<br />
| |
| − | Install ncurses:
| |
| − | <pre>sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dev</pre>
| |
| − | Enable the UHID module compilation:
| |
| − | <pre>cd linux
| |
| − | make menuconfig</pre>
| |
| − | Select Device Drivers>HID support>User-space I/O driver support for HID subsystem.<br />
| |
| − | The line should start with '<M>'.<br />
| |
| − | To speed up the compilation, you can disable all other modules in the HID support section and subsections.<br />
| |
| − | Save the config to the default location and exit.<br />
| |
| − | Build the module:
| |
| − | </pre>make prepare
| |
| − | make scripts
| |
| − | make M=drivers/hid</pre>
| |
| − | Install it:
| |
| − | <pre>sudo cp drivers/hid/uhid.ko /lib/modules/`uname -r`/kernel/drivers/hid/
| |
| − | sudo depmod -a</pre>
| |
| | | | |
| − | <!-- | + | <!--T:26--> |
| − | mkdir dest
| + | The on-board UART runs at 0V/3.3V levels, and the AVR USB board has to run at 5V to operate at 16MHz (running at 3.3V would only allow to operate at 8MHz).<br /> |
| − | make INSTALL_HDR_PATH=dest headers_install
| + | Connecting the RPi and the AVR USB board directly may damage the hardware!<br /> |
| − | sudo cp dest/include/linux/uhid.h /usr/include/linux/
| + | One cheap solution is to use a voltage divider:<br /> |
| − | --> | + | * Connect both GNDs |
| | + | * It's safe to connect the TXD pin of the RPi to the Rx pin of the AVR USB board (the GIMX firmwares configure the Rx pin as an input) |
| | + | * To connect the Tx pin of the AVR USB board to the RXD pin of the RPi, you'll need to convert the voltage level from 0..5V to 0..3.3V.<br /> |
| | + | This can be done with a simple [https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/textbook/direct-current/chpt-6/voltage-divider-circuits/ voltage divider]: |
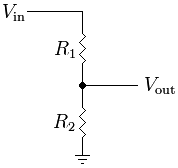
| | + | <div class="image200px">[https://gimx.fr/img/wiki/Resistive_divider.png https://gimx.fr/img/wiki/Resistive_divider.png]</div> |
| | + | Vin is the Tx pin of the AVR USB board, Vout is the RXD pin of the RPi, R1=2.2kΩ , R2=3.3kΩ |
| | + | * Do not connect any other pin! |
| | | | |
| − | == GIMX installation == | + | === Sotware adjustments === <!--T:15--> |
| − | sudo apt-get install gdebi
| |
| − | wget http://gimx.fr/download/gimx-raspbian.html -O gimx.deb
| |
| − | sudo gdebi gimx.deb
| |
| | | | |
| − | == Stop/disable triggerhappy service == | + | <!--T:17--> |
| | + | By default, the RPi UART is configured as a serial console.<br /> |
| | + | Disable this serial console using raspi-config: |
| | + | <pre> |
| | + | sudo raspi-config |
| | + | </pre> |
| | + | Then select: |
| | + | <pre> |
| | + | "Advanced Options", "Serial", "No", "Finish" |
| | + | </pre> |
| | + | The default configuration does not allow high baudrates.<br /> |
| | + | Enable high baudrates editing /boot/config.txt: |
| | + | <pre> |
| | + | sudo nano /boot/config.txt |
| | + | </pre> |
| | + | Add the following line at the end of the file: |
| | + | <pre> |
| | + | init_uart_clock=8000000 |
| | + | </pre> |
| | + | Reboot to apply the changes: |
| | + | <pre> |
| | + | sudo reboot |
| | + | </pre> |
| | + | |
| | + | == GIMX installation == <!--T:7--> |
| | + | <pre>wget https://gimx.fr/download/gimx-raspbian -O gimx.deb |
| | + | sudo dpkg -i gimx.deb |
| | + | sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get -f install</pre> |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:8--> |
| | + | If you get a "Dependency is not satisfiable: ..." error message, upgrade Raspbian: |
| | + | <pre>sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade |
| | + | sudo apt-get -f install</pre> |
| | + | |
| | + | == Stop/disable triggerhappy service == <!--T:9--> |
| | [https://github.com/wertarbyte/triggerhappy/blob/master/README Triggerhappy] is a daemon that opens every input device for reading, and that consumes a few percent of the CPU time. | | [https://github.com/wertarbyte/triggerhappy/blob/master/README Triggerhappy] is a daemon that opens every input device for reading, and that consumes a few percent of the CPU time. |
| | | | |
| | + | <!--T:10--> |
| | It seems a good idea to stop it while running GIMX. | | It seems a good idea to stop it while running GIMX. |
| | | | |
| | + | <!--T:11--> |
| | To stop triggerhappy: | | To stop triggerhappy: |
| | sudo service triggerhappy stop | | sudo service triggerhappy stop |
| Line 82: |
Line 81: |
| | sudo update-rc.d triggerhappy disable | | sudo update-rc.d triggerhappy disable |
| | | | |
| − | == Run GIMX == | + | == Run GIMX == <!--T:12--> |
| | Read the [[Quick_Start|Quick start page]] to learn how to run GIMX through the GUI.<br /> | | Read the [[Quick_Start|Quick start page]] to learn how to run GIMX through the GUI.<br /> |
| − | A good idea is to run GIMX directly from a terminal, without starting a graphical session.<br /> | + | |
| − | This can be done over the network, using a ssh client.<br />
| + | A good idea is to run GIMX directly from a terminal, without starting a graphical session, which can be done over the network, using a ssh client, or you can [[#Autostart GIMX at boot without GUI]]<br /> |
| − | Ideally, GIMX should be launched without using the Ethernet port (because it is connected on the USB bus).<br /> | + | |
| | + | Ideally, GIMX should be launched without using the Ethernet port (because it is connected on the USB bus). However, this doesn't seem to cause any issues generally.<br /> |
| | + | |
| | More details on command line options on [[Command_line|this page]].<br /> | | More details on command line options on [[Command_line|this page]].<br /> |
| − | === Bluetooth === | + | |
| − | Before running GIMX, it is necessary to install the bluez package:
| + | The GUI will help you download the config xmls. If you never run the GUI, you MUST grab the Linux config xmls from here: https://github.com/matlo/GIMX-configurations/tree/master/Linux The Windows xmls are NOT compatible!<br /> |
| − | sudo apt-get install bluez | + | |
| − | In a terminal:
| + | == Autostart GIMX at boot without GUI == <!--T:28--> |
| − | gimx -t Sixaxis -c <config file> -b <PS3 bdaddr> | + | Simply create a file /etc/systemd/system/gimx.service (as root): |
| − | The dongle address has to be changed before running the above commands.
| + | |
| − | === DIY USB adapter === | + | <pre> |
| − | In a terminal: | + | sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/gimx.service |
| − | gimx -c <config file> -p /dev/<ttyUSB port>
| + | </pre> |
| | + | |
| | + | With the following contents: |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:29--> |
| | + | <pre> |
| | + | [Unit] |
| | + | Description=GIMX |
| | + | After=syslog.target network.target |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:30--> |
| | + | [Service] |
| | + | User=pi |
| | + | Type=simple |
| | + | # Replace /dev/ttyUSB0 with /dev/ttyAMA0 when using the on-board UART interface |
| | + | ExecStart=/usr/bin/gimx -p /dev/ttyUSB0 -c LogitechDrivingForceGT_G29.xml --nograb |
| | + | Restart=always |
| | + | RestartSec=5 |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:31--> |
| | + | [Install] |
| | + | WantedBy=multi-user.target |
| | + | </pre> |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:32--> |
| | + | Replace ttyUSB0 with your device (/dev/ttyAMA0 when using the on-board UART interface) and LogitechDrivingForceGT_G29.xml with your mapping file (which should be available in the pi home directory as /home/pi/.gimx/config/LogitechDrivingForceGT_G29.xml) |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:33--> |
| | + | Run <pre>sudo systemctl daemon-reload</pre> to notify systemd about the new file and <pre>sudo systemctl enable gimx && sudo systemctl start gimx</pre> to enable the gimx service start at boot and start it in the same line. |
| | + | |
| | + | == Notify when GIMX is running using a led == <!--T:34--> |
| | + | In order to have a proper confirmation about if the gimx service is up and running, you can add a simple python script that turns a led on if the gimx service is running. |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:35--> |
| | + | The file will be located at /home/pi/blink.py: |
| | + | |
| | + | <pre>sudo nano blink.py</pre> |
| | + | |
| | + | With the following contents: |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:36--> |
| | + | <pre> |
| | + | #!/usr/bin/python |
| | + | import os |
| | + | import time |
| | + | import RPi.GPIO as GPIO |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:37--> |
| | + | led = 23 |
| | + | button = 18 |
| | + | GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) |
| | + | GPIO.setup(led, GPIO.OUT) |
| | + | GPIO.setup(button, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down = GPIO.PUD_UP) |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:38--> |
| | + | def Shutdown(channel): |
| | + | GPIO.output(led, True) |
| | + | time.sleep(0.2) |
| | + | GPIO.output(led, False) |
| | + | time.sleep(0.2) |
| | + | GPIO.output(led, True) |
| | + | time.sleep(0.2) |
| | + | GPIO.output(led, False) |
| | + | os.system("sudo shutdown -h now") |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:39--> |
| | + | GPIO.add_event_detect(18, GPIO.FALLING, callback = Shutdown, bouncetime = 2000) |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:40--> |
| | + | while True: |
| | + | found = False |
| | + | time.sleep(5) |
| | + | pids = [pid for pid in os.listdir('/proc') if pid.isdigit()] |
| | + | for pid in pids: |
| | + | try: |
| | + | cmd = open(os.path.join('/proc', pid, 'cmdline'), 'rb').read() |
| | + | if "gimx" in cmd: |
| | + | found = True |
| | + | except IOError: # proc has already terminated |
| | + | continue |
| | + | if found == True: |
| | + | GPIO.output(led, True) |
| | + | else: |
| | + | GPIO.output(led, False) |
| | + | </pre> |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:41--> |
| | + | As a bonus, you can add a button so when it is pressed, there is a little blink effect, and the pi is shutted down. |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:42--> |
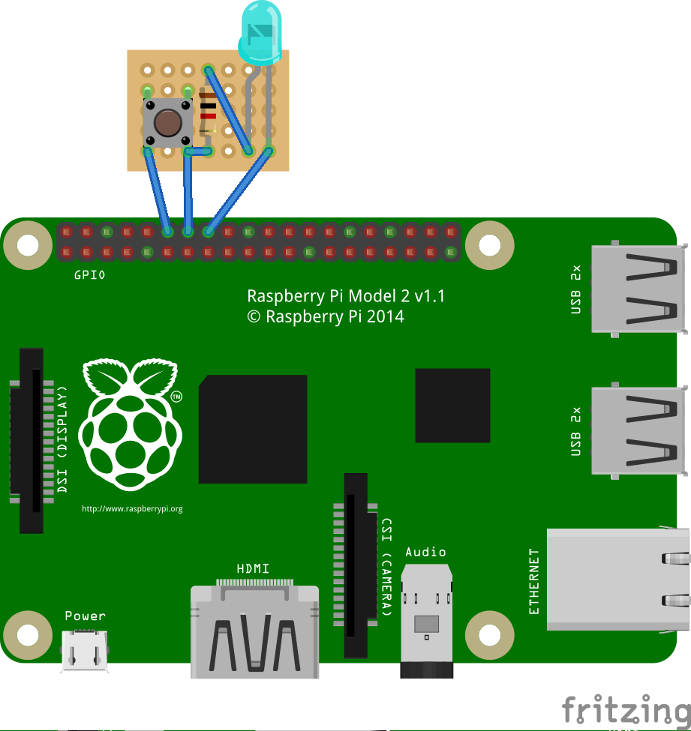
| | + | <div class="image200px">[https://gimx.fr/img/wiki/PiButtonLed.png https://gimx.fr/img/wiki/PiButtonLed.png]</div> |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:43--> |
| | + | To start at boot, simply add it to the pi user crontab (crontab -e) as <pre>@reboot python /home/pi/blink.py &</pre> |
| | + | |
| | + | == Powering on AVR and RPi simultaneously using the on-board UART interface == <!--T:44--> |
| | + | In case you want to power up AVR (Tested on Pro Micro ATmega32u4) and RPi at once (i.e. using PS4 USB port and a USB Y Splitter) using the on-board UART interface, you will need the adjust shown below in order to reset the AVR board from RPi once started. |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:45--> |
| | + | It is planned to solve this issue on GIMX 8 version [https://github.com/matlo/GIMX/issues/426] |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:46--> |
| | + | More details on support forum thread [https://gimx.fr/forum/viewtopic.php?f=5&t=1672] |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:47--> |
| | + | '''Physically''' |
| | + | * RPi's PIN40 / GPIO21 connected to ATmega32u4 RST pin directly. (Any RPi GPIO pin should works) |
| | + | |
| | + | <!--T:48--> |
| | + | '''Logically''' |
| | + | * New bash script created /home/pi/resetArduino.sh with content shown below: |
| | + | <pre> |
| | + | #!/bin/bash |
| | + | |
| | + | echo 21 > /sys/class/gpio/export |
| | + | sleep 1 |
| | + | echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio21/direction |
| | + | sleep 1 |
| | + | echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio21/value |
| | + | sleep 1 |
| | + | echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio21/value |
| | + | sleep 1 |
| | + | echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio21/value |
| | + | |
| | + | exit 0 |
| | + | </pre> |
| | + | * Grant execution permissions |
| | + | <pre>chmod +x /home/pi/resetArduino.sh</pre> |
| | + | * Add the new script to boot sequence (like we do with blink.py program) |
| | + | <pre> |
| | + | pi@raspberrypi:~ $ crontab -l |
| | + | @reboot /home/pi/resetArduino.sh && python /home/pi/blink.py & |
| | + | </pre> |
| | + | |
| | + | Using this configuration, GIMX is able to start correctly on its first attempt when RPi and ATmega32u4 are powered on from PS4 simultaneously using GPIO instead of CP2102 USB UART. |
| | + | |
| | + | </translate> |
Warning: RPi support should be considered as experimental. The USB controller has been unstable since the first version. Be prepared to face issues if you try GIMX on the RPi.
GIMX can run on many Linux targets, and the the Raspberry Pi is one of them!
Setup using pre-made image
The simplest way to set up GIMX on a Raspberry Pi is by flashing a pre-made image. See forum user steel_3d's instructions on getting up and running: Build your own Plug n Play GIMX emulator using Raspberry Pi
Hardware considerations
Use a USB HUB only if there are no ports available on the RPi.
It is highly recommended to use a HUB with an external power supply.
USB adapter using the on-board UART interface
Hardware requirements
The on-board UART runs at 0V/3.3V levels, and the AVR USB board has to run at 5V to operate at 16MHz (running at 3.3V would only allow to operate at 8MHz).
Connecting the RPi and the AVR USB board directly may damage the hardware!
One cheap solution is to use a voltage divider:
- Connect both GNDs
- It's safe to connect the TXD pin of the RPi to the Rx pin of the AVR USB board (the GIMX firmwares configure the Rx pin as an input)
- To connect the Tx pin of the AVR USB board to the RXD pin of the RPi, you'll need to convert the voltage level from 0..5V to 0..3.3V.
This can be done with a simple voltage divider:
Vin is the Tx pin of the AVR USB board, Vout is the RXD pin of the RPi, R1=2.2kΩ , R2=3.3kΩ
- Do not connect any other pin!
Sotware adjustments
By default, the RPi UART is configured as a serial console.
Disable this serial console using raspi-config:
sudo raspi-config
Then select:
"Advanced Options", "Serial", "No", "Finish"
The default configuration does not allow high baudrates.
Enable high baudrates editing /boot/config.txt:
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
Add the following line at the end of the file:
init_uart_clock=8000000
Reboot to apply the changes:
sudo reboot
GIMX installation
wget https://gimx.fr/download/gimx-raspbian -O gimx.deb
sudo dpkg -i gimx.deb
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get -f install
If you get a "Dependency is not satisfiable: ..." error message, upgrade Raspbian:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-get -f install
Stop/disable triggerhappy service
Triggerhappy is a daemon that opens every input device for reading, and that consumes a few percent of the CPU time.
It seems a good idea to stop it while running GIMX.
To stop triggerhappy:
sudo service triggerhappy stop
To disable triggerhappy:
sudo update-rc.d triggerhappy disable
Run GIMX
Read the Quick start page to learn how to run GIMX through the GUI.
A good idea is to run GIMX directly from a terminal, without starting a graphical session, which can be done over the network, using a ssh client, or you can #Autostart GIMX at boot without GUI
Ideally, GIMX should be launched without using the Ethernet port (because it is connected on the USB bus). However, this doesn't seem to cause any issues generally.
More details on command line options on this page.
The GUI will help you download the config xmls. If you never run the GUI, you MUST grab the Linux config xmls from here: https://github.com/matlo/GIMX-configurations/tree/master/Linux The Windows xmls are NOT compatible!
Autostart GIMX at boot without GUI
Simply create a file /etc/systemd/system/gimx.service (as root):
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/gimx.service
With the following contents:
[Unit]
Description=GIMX
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
User=pi
Type=simple
# Replace /dev/ttyUSB0 with /dev/ttyAMA0 when using the on-board UART interface
ExecStart=/usr/bin/gimx -p /dev/ttyUSB0 -c LogitechDrivingForceGT_G29.xml --nograb
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Replace ttyUSB0 with your device (/dev/ttyAMA0 when using the on-board UART interface) and LogitechDrivingForceGT_G29.xml with your mapping file (which should be available in the pi home directory as /home/pi/.gimx/config/LogitechDrivingForceGT_G29.xml)
Run
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
to notify systemd about the new file and
sudo systemctl enable gimx && sudo systemctl start gimx
to enable the gimx service start at boot and start it in the same line.
Notify when GIMX is running using a led
In order to have a proper confirmation about if the gimx service is up and running, you can add a simple python script that turns a led on if the gimx service is running.
The file will be located at /home/pi/blink.py:
sudo nano blink.py
With the following contents:
#!/usr/bin/python
import os
import time
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
led = 23
button = 18
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(led, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(button, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down = GPIO.PUD_UP)
def Shutdown(channel):
GPIO.output(led, True)
time.sleep(0.2)
GPIO.output(led, False)
time.sleep(0.2)
GPIO.output(led, True)
time.sleep(0.2)
GPIO.output(led, False)
os.system("sudo shutdown -h now")
GPIO.add_event_detect(18, GPIO.FALLING, callback = Shutdown, bouncetime = 2000)
while True:
found = False
time.sleep(5)
pids = [pid for pid in os.listdir('/proc') if pid.isdigit()]
for pid in pids:
try:
cmd = open(os.path.join('/proc', pid, 'cmdline'), 'rb').read()
if "gimx" in cmd:
found = True
except IOError: # proc has already terminated
continue
if found == True:
GPIO.output(led, True)
else:
GPIO.output(led, False)
As a bonus, you can add a button so when it is pressed, there is a little blink effect, and the pi is shutted down.
To start at boot, simply add it to the pi user crontab (crontab -e) as
@reboot python /home/pi/blink.py &
Powering on AVR and RPi simultaneously using the on-board UART interface
In case you want to power up AVR (Tested on Pro Micro ATmega32u4) and RPi at once (i.e. using PS4 USB port and a USB Y Splitter) using the on-board UART interface, you will need the adjust shown below in order to reset the AVR board from RPi once started.
It is planned to solve this issue on GIMX 8 version [1]
More details on support forum thread [2]
Physically
- RPi's PIN40 / GPIO21 connected to ATmega32u4 RST pin directly. (Any RPi GPIO pin should works)
Logically
- New bash script created /home/pi/resetArduino.sh with content shown below:
#!/bin/bash
echo 21 > /sys/class/gpio/export
sleep 1
echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio21/direction
sleep 1
echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio21/value
sleep 1
echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio21/value
sleep 1
echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio21/value
exit 0
- Grant execution permissions
chmod +x /home/pi/resetArduino.sh
- Add the new script to boot sequence (like we do with blink.py program)
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ crontab -l
@reboot /home/pi/resetArduino.sh && python /home/pi/blink.py &
Using this configuration, GIMX is able to start correctly on its first attempt when RPi and ATmega32u4 are powered on from PS4 simultaneously using GPIO instead of CP2102 USB UART.